CAT 2020 Slot 3 Question Paper
For the following questions answer them individually
CAT 2020 Slot 3 - Question 21
Five jumbled up sentences, related to a topic, are given below. Four of them can be put together to form a coherent paragraph. Identify the odd one out and key in the number of the sentence as your answer:
1. Machine learning models are prone to learning human-like biases from the training data that feeds these algorithms.
2. Hate speech detection is part of the on-going effort against oppressive and abusive language on social media.
3. The current automatic detection models miss out on something vital: context.
4. It uses complex algorithms to flag racist or violent speech faster and better than human beings alone.
5. For instance, algorithms struggle to determine if group identifiers like "gay" or "black" are used in offensive or prejudiced ways because they're trained on imbalanced datasets with unusually high rates of hate speech.
789
456
123
0.-
Clear All
CAT 2020 Slot 3 - Question 22
Five jumbled up sentences, related to a topic, are given below. Four of them can be put together to form a coherent paragraph. Identify the odd one out and key in the number of the sentence as your answer:
1. The logic of displaying one’s inner qualities through outward appearance was based on a distinction between being a woman and being feminine.
2. 'Appearance' became a signifier of conduct - to look was to be and conformity to the feminine ideal was measured by how well women could use the tools of the fashion and beauty industries.
3. The makeover-centric media sets out subtly and not-so-subtly, ‘good’ and ‘bad’ ways to be a woman, layering these over inequalities of race and class.
4. The denigration of working-class women and women of colour often centres on their perceived failure to embody feminine beauty.
5. ‘Woman’ was considered a biological category, but femininity was a ‘process’ by which women became specific kinds of women.
789
456
123
0.-
Clear All
CAT 2020 Slot 3 - Question 23
The passage given below is followed by four alternate summaries. Choose the option that best captures the essence of the passage.
The dominant hypotheses in modern science believe that language evolved to allow humans to exchange factual information about the physical world. But an alternative view is that language evolved, in modern humans at least, to facilitate social bonding. It increased our ancestors’ chances of survival by enabling them to hunt more successfully or to cooperate more extensively. Language meant that things could be explained and that plans and past experiences could be shared efficiently.
CAT 2020 Slot 3 - Question 24
The passage given below is followed by four alternate summaries. Choose the option that best captures the essence of the passage.
Aesthetic political representation urges us to realize that ‘the representative has autonomy with regard to the people represented’ but autonomy then is not an excuse to abandon one’s responsibility. Aesthetic autonomy requires cultivation of ‘disinterestedness’ on the part of actors which is not indifference. To have disinterestedness, that is, to have comportment towards the beautiful that is devoid of all ulterior references to use - requires a kind of aesthetic commitment; it is the liberation of ourselves for the release of what has proper worth only in itself.
CAT 2020 Slot 3 - Question 25
The passage given below is followed by four alternate summaries. Choose the option that best captures the essence of the passage.
Brown et al. (2001) suggest that ‘metabolic theory may provide a conceptual foundation for much of ecology just as genetic theory provides a foundation for much of evolutionary biology’. One of the successes of genetic theory is the diversity of theoretical approaches and models that have been developed and applied. A Web of Science (v. 5.9. Thomson Reuters) search on genetic* + theor* + evol* identifies more than 12000 publications between 2005 and 2012. Considering only the 10 most-cited papers within this 12000 publication set, genetic theory can be seen to focus on genome dynamics, phylogenetic inference, game theory and the regulation of gene expression. There is no one fundamental genetic equation, but rather a wide array of genetic models, ranging from simple to complex, with differing inputs and outputs, and divergent areas of application, loosely connected to each other through the shared conceptual foundation of heritable variation.
CAT 2020 Slot 3 - Question 26
The four sentences (labelled 1, 2, 3, 4) below, when properly sequenced would yield a coherent paragraph. Decide on the proper sequencing of the order of the sentences and key in the sequence of the four numbers as your answer:
1. Each one personified a different aspect of good fortune.
2. The others were versions of popular Buddhist gods, Hindu gods and Daoist gods.
3. Seven popular Japanese deities, the Shichi Fukujin, were considered to bring good luck and happiness.
4. Although they were included in the Shinto pantheon, only two of them, Daikoku and Ebisu, were indigenous Japanese gods.
789
456
123
0.-
Clear All
Sixteen patients in a hospital must undergo a blood test for a disease. It is known that exactly one of them has the disease. The hospital has only eight testing kits and has decided to pool blood samples of patients into eight vials for the tests. The patients are numbered 1 through 16, and the vials are labelled A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H. The following table shows the vials into which each patient’s blood sample is distributed.
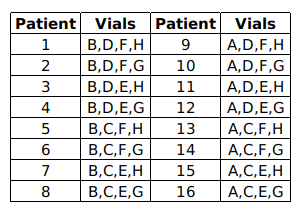
If a patient has the disease, then each vial containing his/her blood sample will test positive. If a vial tests positive, one of the patients whose blood samples were mixed in the vial has the disease. If a vial tests negative, then none of the patients whose blood samples were mixed in the vial has the disease.
CAT 2020 Slot 3 - Question 27
Suppose vial C tests positive and vials A, E and H test negative. Which patient has the disease?
CAT 2020 Slot 3 - Question 28
Suppose vial A tests positive and vials D and G test negative. Which of the following vials should we test next to identify the patient with the disease?
CAT 2020 Slot 3 - Question 29
Which of the following combinations of test results is NOT possible?
CAT 2020 Slot 3 - Question 30
Suppose one of the lab assistants accidentally mixed two patients' blood samples before they were distributed to the vials. Which of the following correctly represents the set of all possible numbers of positive test results out of the eight vials?




