CAT 2024 Slot 3 Question Paper
The passage below is accompanied by four questions. Based on the passage, choose the best answer for each question.
There is a group in the space community who view the solar system not as an opportunity to expand human potential but as a nature preserve, forever the provenance of an elite group of scientists and their sanitary robotic probes. These planetary protection advocates [call] for avoiding “harmful contamination” of celestial bodies. Under this regime, NASA incurs great expense sterilizing robotic probes in order to prevent the contamination of entirely theoretical biospheres ...
Transporting bacteria would matter if Mars were the vital world once imagined by astronomers who mistook optical illusions for canals. Nobody wants to expose Martians to measles, but sadly, robotic exploration reveals a bleak, rusted landscape, lacking oxygen and flooded with radiation ready to sterilize any Earthly microbes. Simple life might exist underground, or down at the bottom of a deep canyon, but it has been very hard to find with robots. . . . The upsides from human exploration and development of Mars clearly outweigh the welfare of purely speculative Martian fungi ...
The other likely targets of human exploration, development, and settlement, our moon and the asteroids, exist in a desiccated, radiation-soaked realm of hard vacuum and extreme temperature variations that would kill nearly anything. It’s also important to note that many international competitors will ignore the demands of these protection extremists in any case. For example, China recently sent a terrarium to the moon and germinated a plant seed—with, unsurprisingly, no protest from its own scientific community. In contrast, when it was recently revealed that a researcher had surreptitiously smuggled super-resilient microscopic tardigrades aboard the ill-fated Israeli Beresheet lunar probe, a firestorm was unleashed within the space community ...
NASA’s previous human exploration efforts made no serious attempt at sterility, with little notice. As the Mars expert Robert Zubrin noted in the National Review, U.S. lunar landings did not leave the campsites cleaner than they found it. Apollo’s bacteria-infested litter included bags of feces. Forcing NASA’s proposed Mars exploration to do better, scrubbing everything and hauling out all the trash, would destroy NASA’s human exploration budget and encroach on the agency’s other directorates, too. Getting future astronauts off Mars is enough of a challenge, without trying to tote weeks of waste along as well.
A reasonable compromise is to continue on the course laid out by the U.S. government and the National Research Council, which proposed a system of zones on Mars, some for science only, some for habitation, and some for resource exploitation. This approach minimizes contamination, maximizes scientific exploration ... Mars presents a stark choice of diverging human futures. We can turn inward, pursuing ever more limited futures while we await whichever natural or manmade disaster will eradicate our species and life on Earth. Alternatively, we can choose to propel our biosphere further into the solar system, simultaneously protecting our home planet and providing a backup plan for the only life we know exists in the universe. Are the lives on Earth worth less than some hypothetical microbe lurking under Martian rocks?
CAT 2024 Slot 3 - Question 21
The author is unlikely to disagree with any of the following EXCEPT:
CAT 2024 Slot 3 - Question 22
The author mentions all of the following reasons to dismiss concerns about contaminating Mars EXCEPT:
CAT 2024 Slot 3 - Question 23
The author’s overall tone in the first paragraph can be described as
CAT 2024 Slot 3 - Question 24
The contrasting reactions to the Chinese and Israeli “contaminations” of lunar space
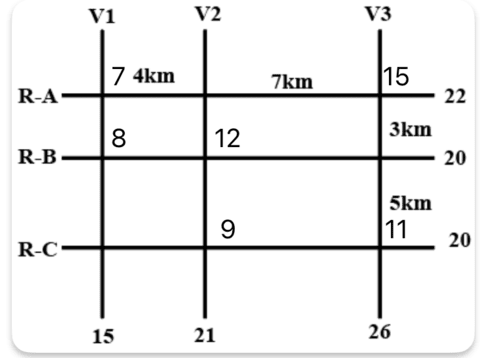
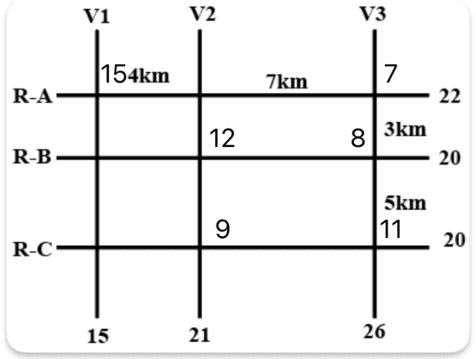
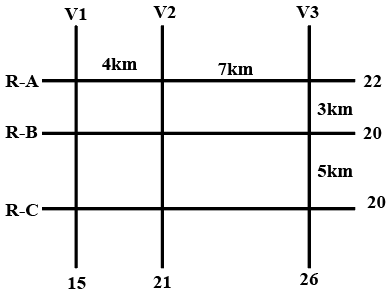
The figure below shows a network with three parallel roads represented by horizontal lines R-A, R-B, and R-C and another three parallel roads represented by vertical lines V1, V2, and V3. The figure also shows the distance (in km) between two adjacent intersections.Six ATMs are placed at six of the nine road intersections. Each ATM has a distinct integer cash requirement (in Rs. Lakhs), and the numbers at the end of each line in the figure indicate the total cash requirements of all ATMs placed on the corresponding road. For example, the total cash requirement of the ATM(s) placed on road R-A is Rs. 22 Lakhs.
The following additional information is known.
1. The ATMs with the minimum and maximum cash requirements of Rs. 7 Lakhs and Rs. 15 Lakhs are placed on the same road.
2. The road distance between the ATM with the second highest cash requirement and the ATM located at the intersection of R-C and V3 is 12 km.
CAT 2024 Slot 3 - Question 26
How many ATMs have cash requirements of Rs. 10 Lakhs or more?
789
456
123
0.-
Clear All
CAT 2024 Slot 3 - Question 27
Which of the following two statements is/are DEFINITELY true?
Statement A: Each of R-A, R-B, and R-C has two ATMs.
Statement B: Each of V1, V2, and V3 has two ATMs.
CAT 2024 Slot 3 - Question 28
What best can be said about the road distance (in km) between the ATMs having the second highest and the second lowest cash requirements?
CAT 2024 Slot 3 - Question 29
What is the number of ATMs whose locations and cash requirements can both be uniquely determined?
789
456
123
0.-
Clear All
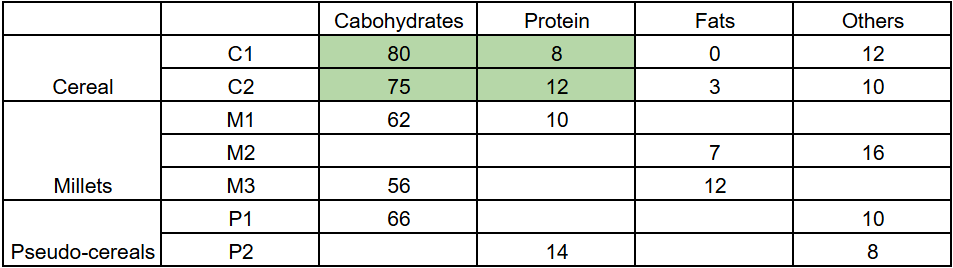
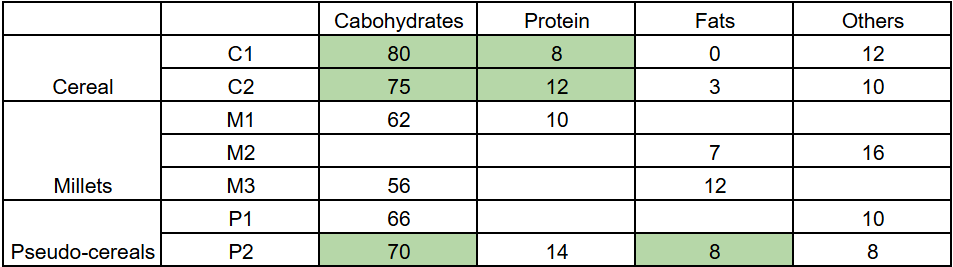
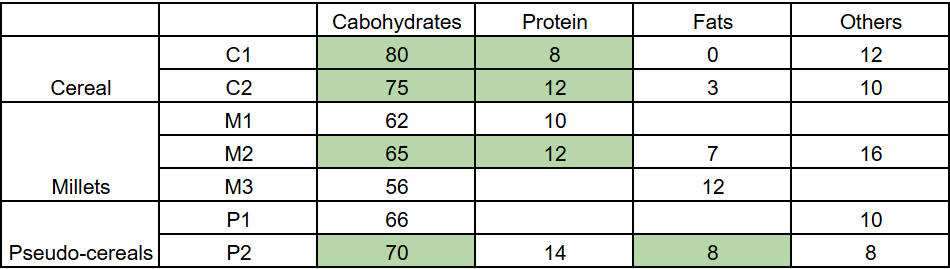
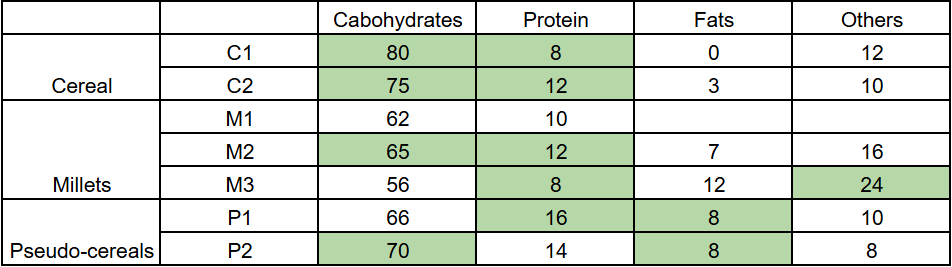
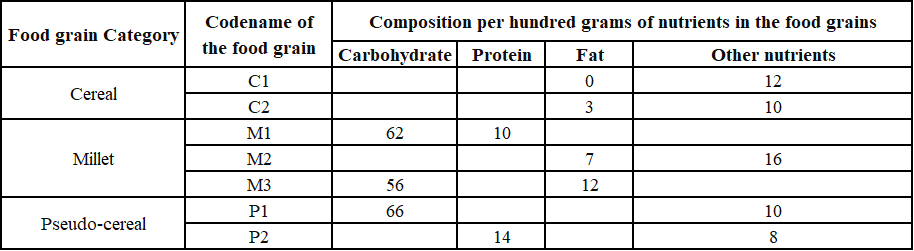
The table given below shows the amount, in grams, of carbohydrate, protein, fat and all other nutrients, per 100 grams of nutrients in seven food grains. The first column shows the food grain category and the second column its codename. The table has some missing values.
The following additional facts are known.
1. Both the pseudo-cereals had higher amounts of carbohydrate as well as higher amounts of protein than any millet.
2. Both the cereals had higher amounts of carbohydrate than any pseudo-cereal.
3. All the missing values of carbohydrate amounts (in grams) for all the food grains are non-zero multiples of 5.
4. All the missing values of protein, fat and other nutrients amounts (in grams) for all the food grains are non-zero multiples of 4.
5. P1 contained double the amount of protein that M3 contains.
CAT 2024 Slot 3 - Question 30
How many foodgrains had a higher amount of carbohydrate per 100 grams ofnutrients than M1?
789
456
123
0.-
Clear All
CAT Quant Questions | CAT Quantitative Ability
CAT DILR Questions | LRDI Questions For CAT
CAT Verbal Ability Questions | VARC Questions For CAT
Also Read
Frequently Asked Questions
You can download the CAT 2024 Slot 3 Question Paper PDF with detailed answers and solutions from Cracku.
Yes, every question in the CAT 2024 Slot 3 paper has step-by-step video solutions for better understanding.
It helps you practice real exam questions, understand difficulty levels, and improve speed and accuracy.
Yes, you can download CAT 2024 Slot 1, Slot 2, and Slot 3 papers in PDF format for complete preparation.
Yes, the solutions and video explanations include simple tricks and smart methods to solve questions quickly.tion.

.png)