Sign in
Please select an account to continue using cracku.in
↓ →
For any non-zero real number x, let $$f(x) + 2f \left(\cfrac{1}{x}\right) = 3x$$. Then, the sum of all possible values of x for which $$f(x) = 3$$, is
We are given, $$f(x) + 2f \left(\cfrac{1}{x}\right) = 3x$$
Substituting $$\frac{1}{x}\ for\ x$$
$$f\left(\dfrac{1}{x}\right)+2f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{3}{x}$$
Multiplying the second equation by 2 we will have
$$2f\left(\dfrac{1}{x}\right)+4f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{6}{x}$$
Subtracting the first equation from the second equation we have,
$$3f\left(x\right)=\frac{6}{x}-3x$$
$$f\left(x\right)=\frac{2}{x}-x$$
We want the sum of values when this function equals 3,
$$\frac{2}{x}-x=3$$
$$x^2+3x-2=0$$
Since the discriminant is greater than zero, both values of x will be real, and we can directly take the sum of values of $$x$$ to be,
$$-\frac{3}{1}$$
Answer is -3.
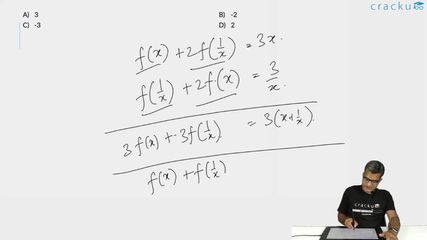
Click on the Email ☝️ to Watch the Video Solution
Create a FREE account and get:
Educational materials for CAT preparation