Sign in
Please select an account to continue using cracku.in
↓ →
The sum of all possible real values of x for which $$\log_{x-3}{(x^{2}-9)}=\log_{x-3}{(x+1)}+2$$, is
Since the base of the logarithm has to be greater than zero and cannot be $$1$$, $$x$$ has to be greater than $$3$$ and cannot be $$4$$. Also, since $$x^2-9>0$$, $$x$$ will be greater than $$3$$.
The equation can be rewritten as;
$$\log_{x-3}{(x^{2}-9)}-\log_{x-3}{(x+1)} = 2$$
Or,
$$\log_{x-3}{\dfrac{x^2-9}{x+1}} = 2$$
$$\Rightarrow \dfrac{(x+3)(x-3)}{x+1} = (x-3)^2$$
$$\Rightarrow \dfrac{(x+3)}{x+1} = (x-3)$$
$$\Rightarrow (x+3) = (x-3)(x+1)$$
$$\Rightarrow x+3 = x^2 - 3x + x - 3$$
$$\Rightarrow x^2 - 3x - 6 = 0$$
The roots of the quadratic above are $$\dfrac{3\pm \sqrt{3^2 + 24}}{2}$$
The negative value of $$x$$ will not be possible, the positive value that satisfies is $$\dfrac{3+ \sqrt{33}}{2}$$
The correct answer is option D.
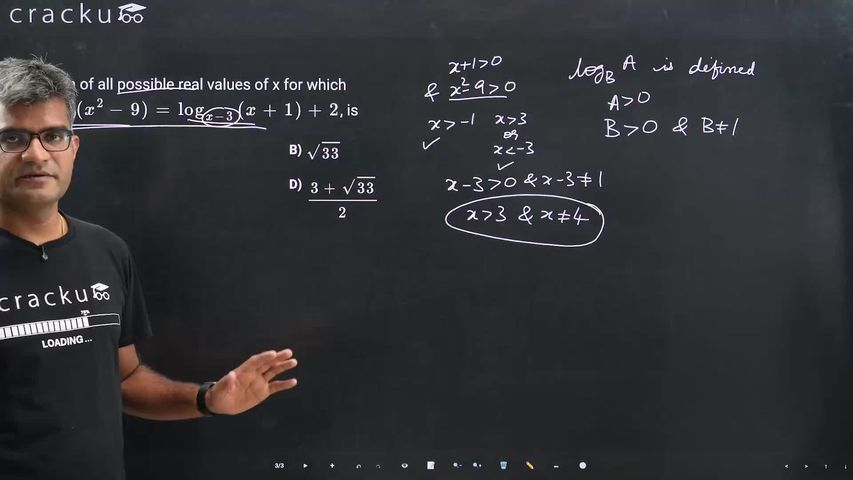
Click on the Email ☝️ to Watch the Video Solution
Create a FREE account and get:
Educational materials for CAT preparation