Sign in
Please select an account to continue using cracku.in
↓ →
ABCD is a trapezium in which AB is parallel to DC, AD is perpendicular to AB, and AB = 3DC. If a circle inscribed in the trapezium touching all the sides has a radius of 3 cm , then the area, in sq. cm, of the trapezium is
We extend $$BC$$ and $$AD$$ to meet at $$E$$, and based on the information provided, can construct the diagram as follows:
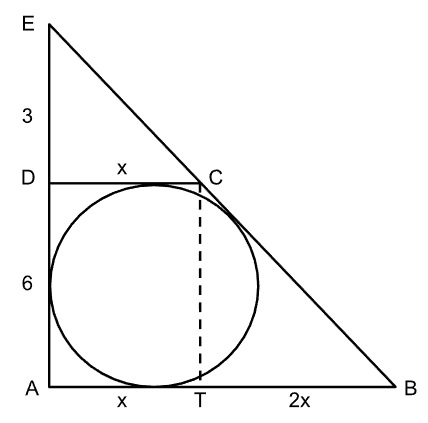
$$DC = AT =x$$ and $$BT = 2x$$ such that $$AB = 3DC$$. $$\angle A= 90^{\circ}$$ and triangles $$ABE$$ and $$DCE$$ are similar.
Since $$AD$$ is equal to the diameter of the circle, and $$AE = 3DE$$, we get $$DE = 3$$ cm.
In right-angled triangle $$DCE$$, we have $$CE = \sqrt{x^2+9}$$
In right-angled triangle $$BCT$$, we have $$BC = \sqrt{4x^2+36} = 2\sqrt{x^2+9}$$
Since $$BE = BC+CE$$, we have $$BE = 3\sqrt{x^2+9}$$
The radius of the incircle of a right-angled triangle is given by $$\dfrac{s_1 + s_2 - \text{hypotenuse}}{2}$$
Therefore, $$3 = \dfrac{3x+9-3\sqrt{x^2+9}}{2}$$
Which gives,
$$-x-1 = -\sqrt{x^2+9}$$ or $$x^2+2x+1 = x^2 + 9$$ or $$x=4$$.
Lastly, the area of the trapezium would be $$\dfrac{1}{2}\times (x+3x) \times 6 = 12x = 12\times 4 = 48$$ square centimetres.
Click on the Email ☝️ to Watch the Video Solution
Create a FREE account and get:
Educational materials for CAT preparation