Sign in
Please select an account to continue using cracku.in
↓ →
In a circle with center C and radius $$6\sqrt{2}$$ cm, PQ and SR are two parallel chords separated by one of the diameters. If $$\angle PQC=45^{0}$$, and the ratio of the perpendicular distance of $$PQ$$ and $$SR$$ from $$C$$ is $$3:2$$, then the area, in sq. cm, of the quadrilateral $$PQRS$$ is
The radius of the circle is given to be $$6\sqrt{2}$$ cm. We are also given that the ratio of CA to CB is 3:2. So, if we assume the value of CA to be 3x, then the value of CB becomes 2x. We are also given that $$\angle PQC=45^{0}$$ and since PCQ is an isosceles triangle, $$\angle CPQ=45^{0}$$ and $$\angle PCQ=90^{0}$$.
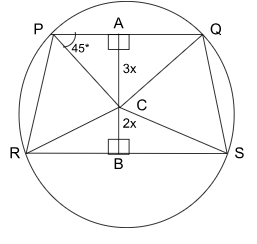
So, the triangle PCQ is right-angled at C. The value of PQ can be calculated using Pythagoras' theorem as,
$$PQ^2\ =\ PC^2\ +\ QC^2$$
$$PQ^2\ =\ \left(6\sqrt{\ 2}\right)^2\ +\ \left(6\sqrt{\ 2}\right)^2\ =\ 72\ +\ 72\ =\ 144$$
$$PQ\ =\ 12$$ cm
$$AQ\ =\ \dfrac{PQ}{2}\ =\ \dfrac{12}{2}\ =\ 6$$ cm
In triangle ACQ,
$$AC^2\ +\ AQ^2\ =\ CQ^2$$
$$\left(3x\right)^2\ +\ \left(6\right)^2\ =\ \left(6\sqrt{\ 2}\right)^2$$
$$9x^2\ +\ 36\ =\ 72$$
$$9x^2\ =\ 36$$
$$x^2\ =\ 4$$
$$x\ =\ 2$$
$$CB\ =\ 2x\ =\ 2\times2\ =\ 4$$ cm
In triangle BCS,
$$BC^2\ +\ BS^2\ =\ CS^2$$
$$\left(4\right)^2\ +\ \left(BS\right)^2\ =\ \left(6\sqrt{\ 2}\right)^2$$
$$16\ +\ \left(BS\right)^2\ =\ 72$$
$$BS^2\ =\ 56$$
$$BS\ =\ 2\sqrt{\ 14}$$ cm
$$RS\ =\ 2\times\ BS\ =\ 2\times\ 2\sqrt{\ 14}\ =\ 4\sqrt{\ 14}$$ cm
The area of the quadrilateral PQRS can be calculated as,
$$Area=\ \dfrac{1}{2}\times\ AB\ \times\ \left(PQ\ +\ RS\right)\ =\ \dfrac{1}{2}\times\ 10\left(12\ +\ 4\sqrt{\ 14}\right)\ =\ 20\left(3\ +\ \sqrt{\ 14}\right)cm^2$$
Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Click on the Email ☝️ to Watch the Video Solution
Create a FREE account and get:
Educational materials for CAT preparation