The figure below shows two right angled triangles ∆OAB and ∆OQP with right angles at vertex A and P, respectively, having the common vertex O, The lengths of some of the sides are indicated in the figure. (Note that the figure is not drawn to scale.) AB and OP are parallel.
What is ∠QOB?
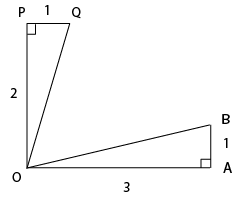
Solution
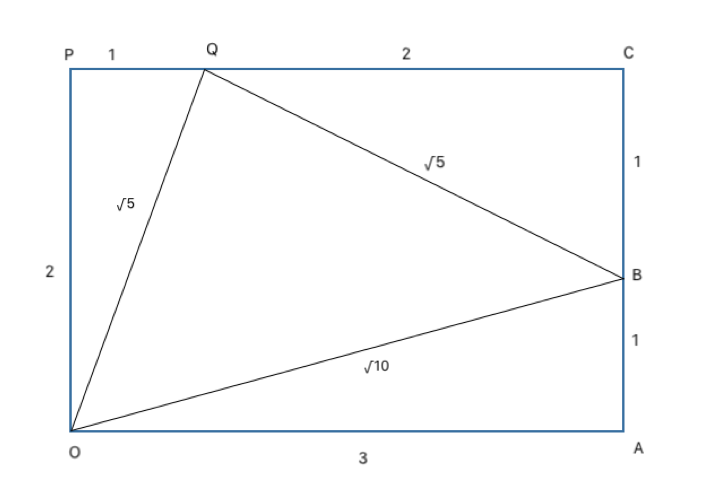
The figure can be redrawn as shown above.
$$\because $$ AB and OP are parallel, POAC is a rectangle.
In right $$\triangle$$QCB, QB = $$\sqrt{5}$$
$$\triangle$$QBO is an isosceles right angled triangle with $$\angle $$OQB = $$ 90°$$ (By Pythagoras theorem)
$$\therefore $$ $$\angle $$QOB = $$45°$$
Video Solution

Click on the Email ☝️ to Watch the Video Solution