A circle is inscribed in an equilateral triangle and a square is inscribed in that circle. The ratio of the areas of the triangle and square is
Solution
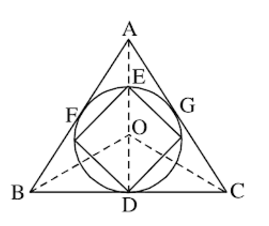
ABC is an equilateral triangle with side $$AB=a$$. AO, BO and CO are the angle bisectors of $$\angle$$ A, $$\angle$$ B and $$\angle$$ C respectively. O is the centre of the circle and let radius of circle = $$r$$ and side of square = $$s$$
Also, we know that the angle bisector from the vertex of an equilateral triangle is the perpendicular bisector of the opposite side.
=> AD is the perpendicular bisector of BC.
=> $$BD=\frac{a}{2}$$ and $$\angle$$ OBD = $$\frac{1}{2}\angle B=\frac{1}{2}\times60^\circ=30^\circ$$
Now, in $$\triangle$$ OBD,
=> $$tan(30^\circ)=\frac{OD}{BD}=\frac{r}{\frac{a}{2}}$$
=> $$r=\frac{1}{\sqrt3}\times\frac{a}{2}=\frac{a}{2\sqrt3}$$
Now, in right $$\triangle$$ EDG, using Pythagoras theorem
=> $$(ED)^2=(EG)^2+(GD)^2$$
=> $$(2r)^2=(s)^2+(s)^2$$
=> $$4r^2=2s^2$$
=> $$s^2=2\times(\frac{a}{2\sqrt3})^2$$
=> $$s^2=\frac{a^2}{6}$$
$$\therefore$$ ar($$\triangle$$) ABC : ar(DEFG)
= $$(\frac{\sqrt3}{4}a^2):(s)^2$$
= $$(\frac{\sqrt3}{4}a^2):(\frac{a^2}{6})$$
= $$3\sqrt3:2$$
=> Ans - (D)
Create a FREE account and get:
- Free SSC Study Material - 18000 Questions
- 230+ SSC previous papers with solutions PDF
- 100+ SSC Online Tests for Free

