Let ABC be a triangle and AD be the perpendicular from the vertex A on the side BC such that $$AD^{2}$$= BDxCD. Then measure of $$\ \angle\ $$BAC is:
Solution
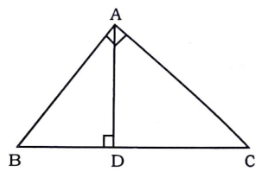
Given : In $$\triangle ABC$$, $$AD \perp BC$$and $$AD^2=BD\times DC$$
To find : $$\angle BAC$$
Solution : In right $$\triangle$$ ADB and $$\triangle$$ ADC, if we apply Pythagoras Theorem,
=> $$(AB)^2=(AD)^2+(BD)^2$$ -------------(i)
and => $$(AC)^2=(AD)^2+(DC)^2$$ -------------(ii)
Adding equations (i) and (ii), we get :
=> $$(AB)^2+(AC)^2=2(AD)^2+(BD)^2+(DC)^2$$
=> $$(AB)^2+(AC)^2=2(BD)(DC)+(BD)^2+(DC)^2$$ [Given]
=> $$(AB)^2+(AC)^2=(BD+DC)^2$$
=> $$(AB)^2+(AC)^2=(BC)^2$$
Hence, $$\triangle$$ ABC is a right triangle right angled at A.
$$\therefore$$ $$\angle$$ BAC = $$90^\circ$$
=> Ans - (A)
Create a FREE account and get:
- Free SSC Study Material - 18000 Questions
- 230+ SSC previous papers with solutions PDF
- 100+ SSC Online Tests for Free

