Impact of GST on Indian Economy PDF 2018 gives you the complete details about impact of Good and Services Tax in India and also the History of GST Bill in India. This blog also covers impact for the Indian Consumers. This Blog will be very useful for GK preparation and also for interviews of Banking exams like IBPS, RRB, SBI, RRB (PO and Clerk) and also UPSC exams. Take a free mock test for SBI Clerk to practice GK questions on this topic. GST topic is very important as you can see in the SBI Clerk Previous Solved papers.
Download RBI Grade B Study Material
Download Financial Institutions in India and World Notes PDF
[icegram campaigns=”7908″]
You can download the Impact of GST on Indian Economy PDF or you can go through this excellent Blog.
Download Impact of GST on Indian Economy PDF
Download RBI Grade B detailed syllabus PDF
Complete Details about GST in India
- What is GST and when is it introduced?
GST Stands for Goods and Services Tax (GST). The GST Act was passed in the Lok Sabha on 29th March, 2017 and came into effect from 1st July, 2017. It was termed as One Nation One Tax.
75 SBI Clerk Mocks & Sectionals – Rs. 360
- Why is GST making so much of News?
GST was introduced as The Constitution (One Hundred and First Amendment) Act 2017 following the passage of Constitution 122nd Amendment Bill. It is an Indirect Tax applicable throughout India which replaced multiple taxes (like Service Tax, Vat Tax) levied by Central & State Governments of India.
- How does GST works? (In Layman terms)
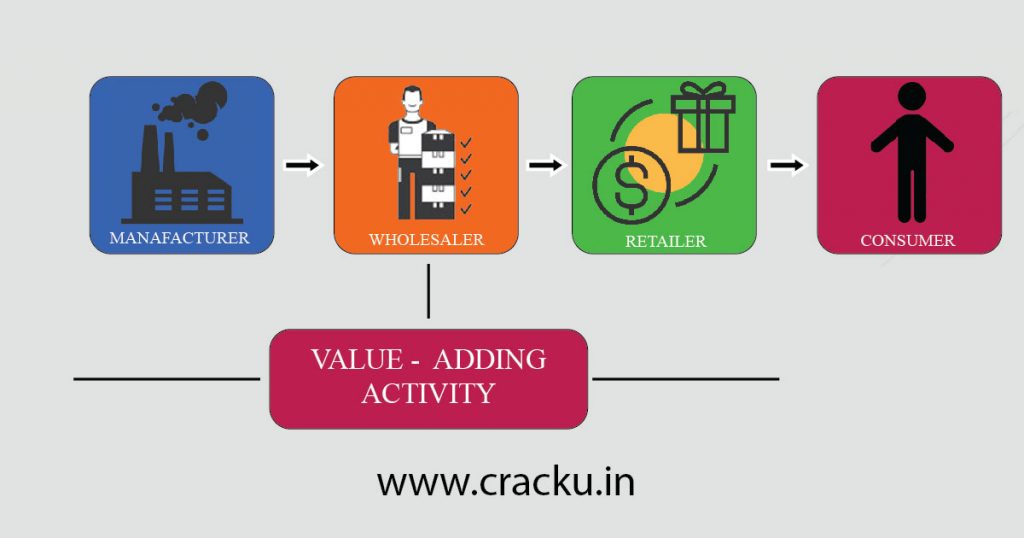
Before Introducing GST:
Suppose say a manufacturer buys raw material from a Vendor. He needs to pay a VAT (Value Added Tax-12.5%) along with the cost of the product. The manufacturer incurs some cost to produce the product. He then adds some profit to it and sells it to Wholesaler. The Whole Saler again needs to pay tax (VAT+Excise Duty=12.5%+12.5%=25%) on the product. The Wholesaler again adds some profit on the product before selling the product to retailer. The Retailer again needs to pay VAT (12.5%) for this product. Then he adds some profit margin and again sells it to customers. For the same product before reaching customers hands multiple taxes are levied and the cost of the product increases significantly.
After GST Bill Implementation:
GST Law has replaced many indirect tax laws that previously existed in India. In place of VAT, Service Tax etc the Government has Come up with Central GST & State GST (12%+12%).
Suppose say the manufacturer after adding his profit sells the product to the Wholesaler at Rs.140. The Wholesaler then sells the product to the retailer at Rs.154 after adding a profit of 10% margin. The retailer then again adds 10% as profit which makes the cost of the product Rs.169.5 and a 12% CGST + 12% SGST is added to this product which the cost of the product stand at Rs.210.18. So, by the implementation of GST the cost of the product can be reduced.
Before GST, tax on tax was calculated and tax was paid by every purchaser including the final consumer. The taxation on tax is called the Cascading Effect of Taxes. But GST is payable at the final point of consumption, meaning that the ‘taxable event’ will be the ‘supply of goods’ and the ‘supply of services’.
SBI Clerk Previous Solved Papers
- What are the taxes GST replaced?
At Central Level:
- Central Excise Duty
- Additional Excise Duty
- Service Tax
- Additional Customs Duty commonly known as Countervailing Duty
- Special Additional Duty of Customs
At State Level:
- Subsuming of State Value Added Tax/Sales Tax
- Entertainment Tax (other than the tax levied by the local bodies), Central Sales Tax (levied by the Centre and collected by the States),
- Octroi and Entry tax
- Purchase Tax
- Luxury Tax
- Taxes on lottery, betting and gambling.
Brief history of GST in India
- Goods and Services Tax (GST) was first proposed in 1999 during a meeting between then Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee and his economic advisory panel, which included three former RBI governors IG Patel, Bimal Jalan and C Rangarajan. Vajpayee set up a committee headed by the then finance minister of West Bengal, Asim Dasgupta to design a GST model.
- After 2004 general elections, during the Congress-led UPA government, the then Finance Minister P.Chidambaram in February 2006 continued work on the same and proposed a GST rollout by 1 April 2010.
- In 2014, the NDA government was re-elected into power and the GST Act was passed in the Lok Sabha on 29th March, 2017 and came into effect from 1st July, 2017.
100 Free General Knowledge Tests for Banking Exams
- How would GST be administered in India?
The GST is governed by a GST Council and its Chairman is the Finance Minister of India. Keeping in mind the federal structure of India, there will be two components of GST – Central GST (CGST) and State GST (SGST). Both Centre and States will simultaneously levy GST across the value chain. Thats why there is Very hight Impact of GST on Indian Economy.
- What are the various slabs of GST in India?
GST slabs are pegged at 5%, 12%, 18% & 28%. The products like Milk, Curd, Lassi, Eggs, Unpacked Food Grains, Fresh Vegetables, Prasad, Salt, Khadi purchased from Khadi and Village Industries stores, Clay idols, brooms, Cotton seed oil cake, Charkha. Hotels and lodges with tariff below Rs 1,000, Educational & Health Services, Grandfathering service has been exempted under GST. Goods like petroleum, alcohol and tobacco are excluded.
Download List of all Schemes of Indian Government PDF
- What are the Advantages of GST on Indian Economy?
- Life gets simpler- GST will replace 17 indirect tax levies and compliance costs will fall.
- Revenue will get a boost- Evasion set to drop – Input tax credit will encourage suppliers to pay taxes – States and Centre will have dual oversight – The number of tax-exempt goods will decline
- A common market-It’s currently fragmented along state lines, pushing costs up 20-30%
- Increased efficiency in Logistics: At the state borders slow movement of trucks. In India, they travel 280 km a day?? compared with 800 km in the US
- Investment boost-For many capital goods, input tax credit is not available.
- Boost for E-Commerce Sector- Freeing up online State restrictions.
- Make in India (a) Manufacturing will get more competitive as GST addresses cascading of tax, inter-state tax, high logistics costs and fragmented market.
(b)Increased protection from imports as GST provides for appropriate countervailing duty. - Less developed states get a lift- The current 2% inter-state levy means production is kept within a state. Under the GST national market, this can be dispersed, creating opportunities for others.
- What are the short Comings of GST?
- Increased costs due to software purchase
- Being GST-compliant
- GST will mean an increase in operational costs
- GST came into effect in the middle of the financial year
- GST is an online taxation system
- SMEs will have a higher tax burden
GK Questions and Answers for Competitive exams PDF
- What are the widely used products that have become cheaper after GST?
FMCG products like Bathing & Washing soaps, Hair oil, Detergent powder, Tissue papers, Napkins, Matchsticks, Kerosene, LPG domestic, Agarbatti, Toothpaste.
Stationery items like pens, books, pencils School Bags, Printer, Papers.
Healthcare items like Insulin, X-ray films for medical use, Diagnostic kits Glasses for corrective spectacles, Medicines for diabetes, cancer.
Apparels like Silk, Woollen fabrics, Khadi yarn, Gandhi topi, Footwear below Rs 500, Apparel up to Rs 1,000
- What are the widely used products that have become dearer after GST?
Ghee, Cold drinks, Chocolate, Packaged chicken, Ice cream, Ayurvedic medicines, Movie tickets greater than Rs 100, AC restaurants, Electronic Home Appliances, Furniture, Cell phone bill, Insurance premiums, Bank services, credit card services, IPL tickets, AC train tickets, Business class air travels, Advertising services, Motorbikes with more than 350 cc engine, Telecom, Hotel room more than Rs 5,000, five star hotel restaurants. This is how the GST impacted Indian economy.
Download Commissions in India and their Heads PDF
- GST in India vs GST in Other Countries
The Indian GST case is structured for efficient tax collection, reduction in corruption, easy inter-state movement of goods etc. France was the first country to implement GST to reduce tax- evasion. Since then, more than 160 countries have implemented GST with some countries having Dual-GST (e.g. Brazil, Canada etc.) model. India has chosen the Canadian model of dual GST.
However, the one big difference between the Indian model of GST and similar taxes in other countries is the dual GST model. Many countries in the world have a single unified GST system, countries like Brazil and Canada have a dual GST system whereby GST is levied by both the federal and state or provincial governments. In India, a dual GST is proposed whereby a Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) and a State Goods and Services Tax (SGST) will be levied on the taxable value of every transaction of supply of goods and services. So Impact of GST is very high on the Common man.
- How will IT be used for the implementation of GST Bill?
For the implementation of GST in the country, the Central and State Governments have jointly registered Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN) as a not-for-profit, non-Government Company to provide shared IT infrastructure and services to Central and State Governments, tax payers and other stakeholders. The key objectives of GSTN are to provide a standard and uniform interface to the taxpayers, and shared infrastructure and services to Central and State/UT governments.
Download Cabinet ministers of India PDF
- What are the penalties if GST is not payed or evaded?
Penalties may be imposed if the following offences are committed:
- Any deficiency on the net tax payable.
- No GST return is made.
- A GST return is submitted without payment or a lesser payment;
- Any refund paid to which there is no proper entitlement.
- Failure to register.
So GST Bill have very high impact on the Indian economy.
- Latest News:
- A proposal is put by the opposition parties to bring petroleum products under GST.
- The government has launched an app called GST Rate Finder for calculating all the tax rates levied under the GST (Goods and Services Tax) regime. The app has been developed by the Central Board of Excise and Custom (CBEC).
- Impact of GST on Indian Economy PDF – Other important Facts:
- India has chosen the Canadian model of dual GST.
- France was the first country to implement in 1954.
As you have gone through the Impact of GST on Indian Economy PDF, you can also download all our GK and Current Affairs Questions and answers PDF.






[…] Impact of GST on Indian Economy PDF – September 21st, 2017 […]