Maths Questions for SSC CGL Tier – 2 PDF
Download SSC CGL Tier 2 Maths Questions PDF. Top 20 Maths questions based on previous exam papers very important for the SSC exam.
Download Maths Questions for SSC CGL Tier – 2 PDF
Get 10 SSC CGL Tier-2 Mocks for Rs. 149
Take SSC CGL Tier-2 Mock Tests
Download SSC CGL Tier-2 Previous Papers PDF
Question 1: Three persons A, B and C have different amounts of rupees with them. If A takes ₹6 from C, A will have equal amount as B has. A and B together have total ₹74. How many rupees does B have ?
a) 44
b) 30
c) 40
d) 34
Question 2: The difference between the Mode and the Median of a data is 25. What is the difference between the Median and the Mean?
a) 10.5
b) 16
c) 12.5
d) 14
Question 3: A dice is rolled two times. Find the probability of getting a composite number on first roll and a prime number on second roll?
a) $\frac{1}{2}$
b) $\frac{1}{6}$
c) $\frac{1}{9}$
d) $\frac{1}{4}$
Question 4: AB is a tangent to a circle with centre O. If the radius at the circle is 7 cm and the length of AB is 24 cm, the what is the length (in cm.) of OA ?
a) 25
b) 26
c) 28
d) 31
Question 5: What Is the compound interest (in Rs.) on a principal sum of Rs. 2800 for 2 years at the rate of 12% per annum?
a) 687.18
b) 634.46
c) 712.32
d) 568.68
Take SSC CGL Tier-2 Mock Tests
Question 6: One third of a certain journey is covered at the speed of 80 km/hr, one fourth of the journey at the speed of 50 km/hr And the rest at the speed of 100 km/hr, what will be the average speed (in km/hr) for the whole journey ?
a) 75
b) 67
c) 66.66
d) 76.66
Question 7: The marked price of an article is Rs. 8480. If a discount of 12.5% is given, then what will be the selling price (in Rs.) of the article ?
a) 7420
b) 6890
c) 6360
d) 7380
Question 8: Pipe A can fill a tank in 12 hours and pipe B can fill the tank in 18 hours. If both the pipes are opened on alternate hours and if pipe B is opened first, then in how much time (in hours) the tank will be full?
a) $14\frac{1}{3}$
b) $14\frac{2}{3}$
c) $14\frac{1}{2}$
d) $14\frac{2}{5}$
Question 9: A certain amount grows at an annual interest rate of 12%, compounded monthly. Which of the following equations can be solved to find the number of years, y, that it would take for the investment to increase by a factor of 64 ?
a) $64=(1.01)^{12y}$
b) $\frac{1}{64}= (1.04)12y$
c) $64=(1.04)^{12y}$
d) $8=(1.01)^{6y}$
Question 10: A balance of a trader weighs 20% less than it should be. Still the trader mark-up his goods to get the overall profit of 35%. What is mark-up on the cost price ?
a) 7%
b) 8%
c) 9%
d) 8.5%
Download SSC CGL Tier-2 Previous Papers PDF
Take SSC CGL Tier-2 Mock Tests
Question 11: Chord PQ is the perpendicular bisector of radius OA of circle with center O (A is a point on the edge of the circle). If the length of Arc PAQ = $\frac{2\pi}{3}$. What is the length of chord PQ ?
a) 2
b) $\sqrt{3}$
c) $2\sqrt{3}$
d) 1
Question 12: A vertical pole AB is standing at the centre B of a square PQRS. If PR subtends an angle of $90^{0}$at the top A of the pole, then the angle subtended by a side of the square at A is:
a) $30^{0}$
b) $45^{0}$
c) $60^{0}$
d) None of these
Question 13: Anil started a business with an investment of Rs. 25,000. After 3 months, Vishal joined his business with a capital of Rs. 30,000. At the end of the year, they have made a profit of Rs. 19,000. What will be Anil’s share in the profit ?
a) Rs. 10,000
b) Rs. 12,500
c) Rs. 10,250
d) Rs. 14,000
Question 14: If $\frac{\sin \theta}{1 + \cos \theta} + \frac{1 + \cos \theta}{\sin \theta} = \frac{4}{\sqrt{3}}, 0^\circ < \theta < 90^\circ$, then the value of $(\tan \theta + \sec \theta)^{-1}$ is:
a) $2 – \sqrt{3}$
b) $3 – \sqrt{2}$
c) $2 + \sqrt{3}$
d) $3 + \sqrt{2}$
Question 15: The value of $\left(\frac{sinA}{1-cosA} + \frac{1-cosA}{sinA}\right) \div \left(\frac{cot^2A}{1+cosecA} + 1\right)$ is:
a) $\frac{3}{2}$
b) $\frac{1}{2}$
c) 1
d) 2
Download SSC CGL General Science Notes PDF
Question 16: The greatest number that will divide 146, 248 and 611 leaving remainders 2,8 and 11 respectively is:
a) 47
b) 144
c) 24
d) 612
Question 17: What is the ratio between the fourth proportional to 1.2, 2.8 and 3.3 and the mean proportional between 1.6 and 48.4?
a) 7:8
b) 4:5
c) 11:12
d) 6:7
Question 18: The 3rd and 6th term of an arithmetic progression are 13 and -5 respectively. What is the 11th term?
a) -29
b) -41
c) -47
d) -35
Question 19: If $\sin \theta = \sqrt{3} \cos \theta, 0^\circ < \theta < 90^\circ$, then the value of $2 \sin^2 \theta + \sec^2 \theta + \sin \theta \sec \theta + cosec \theta$ is:
a) $\frac{33 + 10\sqrt{3}}{6}$
b) $\frac{19 + 10\sqrt{3}}{6}$
c) $\frac{33 + 10\sqrt{3}}{3}$
d) $\frac{19 + 10\sqrt{3}}{3}$
Question 20: An amount is distributed among Sona, Mona and Raj such as the amount obtained by Mona is 92% of the amount obtained by Sona. The ratio between the amount obtained by Mona and Raj is 23:39 respectively. If the difference between the amount obtained by Sona and Raj is Rs. 434 . Then find out the amount obtained by Mona.
a) Rs. 771
b) Rs. 789
c) Rs. 747
d) Rs. 713
18000+ Questions – Free SSC Study Material
Free SSC Preparation (Videos Youtube)
Answers & Solutions:
1) Answer (C)
Let initially, A has $₹ x$, B has $₹ y$ and C has $₹ z$
According to question,
$x+6 = y$ and $x+y = 74$,
So by solving equation, We get
$\therefore y=40$
2) Answer (C)
We now that 3 median -2 mean=mode
Given mode-median=25
mode=median+25
therefore 3 median-2 mean=median+25
2 median-2 mean=25
median-mean=12.5
3) Answer (B)
Number of composite numbers in a dice = 2 (4 and 6)
Hence, Probability of getting a composite number = $\dfrac{2}{6} = \dfrac{1}{3}$
Number of prime numbers in a dice = 3 (2, 3 and 5)
Hence, Probability of getting a prime number = $\dfrac{3}{6} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Therefore, probability of getting a composite number on first roll and a prime number on second roll = $\dfrac{1}{3}\times\dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{1}{6}$
4) Answer (A)
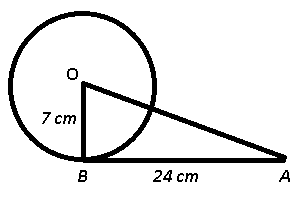
Given : OB is radius of circle = 7 cm and tangent AB = 24 cm
To find : OA = ?
Solution : The radius of a circle intersects the tangent at right angle, => $\angle OBA = 90^\circ$
Thus in $\triangle$ OAB,
=> $(OA)^2=(OB)^2+(AB)^2$
=> $(OA)^2=(7)^2+(24)^2$
=> $(OA)^2=49+576=625$
=> $OA=\sqrt{625}=25$ cm
=> Ans – (A)
5) Answer (C)
Principal sum = Rs. 2800
Rate of interest = 12% and time = 2years
Compound interest = $P[(1+\frac{R}{100})^T-1]$
= $2800[(1+\frac{12}{100})^2-1]$
= $2800[(\frac{28}{25})^2-1]$
= $2800\times(\frac{784-625}{625})$
= $2800\times\frac{159}{625}=Rs.$ $712.32$
=> Ans – (C)
6) Answer (A)
Let the total distance = $12x$ km
Distance covered at 80 km/hr = $\frac{12x}{3}=4x$ km
=> Time taken = $\frac{4x}{80}=\frac{x}{20}$ hours
Distance covered at 50 km/hr = $\frac{12x}{4}=3x$ km
=> Time taken = $\frac{3x}{50}$ hours
Distance covered at 100 km/hr = $12x-4x-3x=5x$ km
=> Time taken = $\frac{5x}{100}=\frac{x}{20}$ hours
Thus, total time = $\frac{x}{20}+\frac{3x}{50}+\frac{x}{20}$
= $\frac{x}{10}+\frac{3x}{50}=\frac{8x}{50}$
$\therefore$ Average speed = total distance/total time
= $\frac{12x}{\frac{8x}{50}}$
= $12\times\frac{50}{8}=75$ km/hr
=> Ans – (A)
7) Answer (A)
Marked price = Rs. 8480 and discount % = 12.5%
=> Selling price = $8480-\frac{12.5}{100}\times8480$
= $8480-\frac{8480}{8}=8480-1060$
= $Rs.$ $7420$
=> Ans – (A)
8) Answer (C)
Let capacity of tank = L.C.M. (12,18) = 36 litres
Pipe A can fill a tank in 12 hours, => Pipe A’s efficiency = $\frac{36}{12}=3$ litres/hr
Similarly, pipe B’s efficiency = $\frac{36}{18}=2$ litres/hr
Now, in 2 hours tank filled is (B opened first) = $2+3=5$ litres
$\because$ $5\times7=35$, hence 35 litres of tank is filled in 14 hours.
Now, B is opened and it will fill the remaining 1 litre in $\frac{1}{2}$ hour.
$\therefore$ Total time taken = $14\frac{1}{2}$ hours
=> Ans – (C)
9) Answer (A)
Rate of interest = 12% p.a. = 1% per month
Time = $12y$ months
Let principal = Re 1 and thus amount = Rs. 64
$\therefore$ $A=P(1+\frac{R}{100})^T$
=> $64=1(1+\frac{1}{100})^{12y}$
=> $64=(1.01)^{12y}$
=> Ans – (A)
10) Answer (B)
Profit % = 35%
Thus, mark up on cost price = $[35-20-(\frac{35\times20}{100})]\%$
= $15-7=8\%$
=> Ans – (B)
11) Answer (B)
.
PQ is perpendicular bisector of OA. Also, OP = OQ (radii)
Hence, OPAQ is a rhombus. ————–(i)
Also, $2\angle PAQ=$ reflex $\angle POQ$ [The angle subtended at the centre by an arc is twice to that at the circumference]
=> $2\angle PAQ=360^\circ-\angle POQ$
=> $2\angle PAQ+\angle POQ=360^\circ$
From (i), we have $\angle PAQ=\angle POQ$
=> $3\angle POQ=360^\circ$
=> $\angle POQ=120^\circ=\frac{2\pi}{3}$
We know that, $r=\frac{l}{\theta}$
=> $r=\frac{\frac{2\pi}{3}}{\frac{2\pi}{3}}=1$ unit
In $\triangle$ POB,
=> $sin(\angle POB)=\frac{PB}{OP}$
=> $sin(60^\circ)=\frac{PB}{1}$
=> $PB=\frac{\sqrt3}{2}$
$\therefore$ Chord PQ = $2\times(PB)=2\times\frac{\sqrt3}{2}=\sqrt3$
=> Ans – (B)
12) Answer (C)
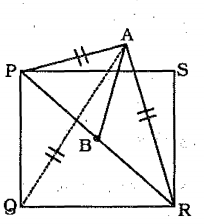
The pole is standing at the centre of the square, => PA = PR
=> $\angle$ APB = $\angle$ ARB = $45^\circ$
Let the side of the square = $x$ units
=> PR (diagonal) = $\sqrt2x$ units
Hence, PB = $\frac{x}{\sqrt2}$ units
Now, in $\triangle$ APB,
=> $tan(\angle APB)=\frac{AB}{PB}$
=> $tan(45^\circ)=1=\frac{AB}{PB}$
=> $AB=PB=\frac{x}{\sqrt2}$
Thus, $PA=\sqrt{(\frac{x}{\sqrt2})^2+(\frac{x}{\sqrt2})^2}$
=> $PA=\sqrt{\frac{x^2}{2}+\frac{x^2}{2}}=\sqrt{x^2}=x$
Similarly, $QA=x$ units
Hence, PA = PQ = QA = $x$
$\therefore$ $\angle$ PAQ = $60^\circ$
=> Ans – (C)
13) Answer (A)
Anil invested Rs. 25,000 for 12 months and Vishal invested Rs. 30,000 for 9 months
=> Ratio of profits = $(25,000\times12):(30,000\times9)$
= $300:270=10:9$
Total profit = Rs. 19,000
$\therefore$ Anil’s share in the profit = $\frac{10}{(10+9)}\times19,000$
= $10\times1000=Rs.$ $10,000$
=> Ans – (A)
14) Answer (A)
$\frac{\sin \theta}{1 + \cos \theta} + \frac{1 + \cos \theta}{\sin \theta} = \frac{4}{\sqrt{3}}$
Put the $\theta = 60\degree$,
$\frac{\sin 60\degree}{1 + \cos 60\degree} + \frac{1 + \cos 60\degree}{\sin 60\degree} = \frac{4}{\sqrt{3}}$
$\frac{\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}}{1 +\frac{1}{2}} + \frac{1 + \frac{1}{2}}{\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}} = \frac{4}{\sqrt{3}}$
$\frac{\frac{3}{4} + \frac{9}{4}}{\frac{3}{2} \times \frac{3}{4}} = \frac{4}{\sqrt{3}}$
$\frac{4}{\sqrt{3}} = \frac{4}{\sqrt{3}}$
Now,
$(\tan \theta + \sec \theta)^{-1}$
Put the $\theta = 60\degree$,
= $(\tan 60\degree + \sec 60\degree)^{-1}$
= $(\sqrt{3} + 2)^{-1}$
= $2 – \sqrt{3}$
15) Answer (D)
$\left(\frac{sinA}{1-cosA} + \frac{1-cosA}{sinA}\right) \div \left(\frac{cot^2A}{1+cosecA} + 1\right)$
Let the value of $\theta = 45\degree$,
$\left(\frac{\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}}{1- \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}} + \frac{1- \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}}{\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}}\right) \div \left(\frac{1}{1+\sqrt{2}} + 1\right)$
=$\left(\frac{\frac{1}{2} + (1- \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}})^2}{(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}})(1- \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}})}\right) \div \left(\frac{1 + 1+\sqrt{2}}{1+\sqrt{2}}\right)$
= $\left(\frac{\frac{1}{2} + 1 + \frac{1}{2} – \sqrt{2}}{(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}})(1- \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}})}\right) \div \left(\frac{2+\sqrt{2}}{1+\sqrt{2}}\right)$
= $\left(\frac{2 – \sqrt{2}}{(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}- \frac{1}{2})}\right) \div \left(\frac{2+\sqrt{2}}{1+\sqrt{2}}\right)$
= $\left(\frac{2 – \sqrt{2}}{\frac{2 – \sqrt{2}}{2\sqrt{2}}}\right) \div \left(\frac{2+\sqrt{2}}{1+\sqrt{2}}\right)$
= $2\sqrt{2} \times \frac{1+\sqrt{2}}{2+\sqrt{2}}$ = 2
16) Answer (C)
The greatest number that will divide 146, 248 and 611 leaving remainders 2,8 and 11 respectively
= H.C.F. of (146-2), (248-8), (611-11)
= H.C.F. (144,240,600) = 24
=> Ans – (C)
17) Answer (A)
The fourth proportional to 1.2, 2.8 and 3.3 is $\dfrac{2.8\times3.3}{1.2} = 7.7$
The mean proportion between 1.6 and 48.4 is $\sqrt{1.6\times48.4} = 8.8$
Therefore, The required ratio = 7.7:8.8 = 7:8.
18) Answer (D)
$T_{3}$ = a + 2d = 13——-(1)
$T_{6}$ = a + 5d = -5——-(2)
on solving (1) AND (2)
d = -6 & a = 25
$T_{11}$ = a + 10d = 25 + 10(-6) = -35
so the answer is option D.
19) Answer (A)
$\sin \theta = \sqrt{3} \cos \theta, 0^\circ < \theta < 90^\circ$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\sin \theta}{\cos \theta} = \sqrt{3}$
$\Rightarrow \tan \theta = \sqrt{3}$
$\Rightarrow \theta = 60\degree$
Now,
$2 \sin^2 \theta + \sec^2 \theta + \sin \theta \sec \theta + \cosec \theta$
= $2 \sin^2 60\degree + \sec^2 60\degree + \tan 60\degree + \cosec60\degree$
= $2 \times (\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2})^2 + 2^2 + \sqrt{3} + \frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}$
= $\frac{3}{2} + 4 + \sqrt{3} + \frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}$
= $\frac{3\sqrt{3} + 8\sqrt{3} + 6 + 4}{2\sqrt{3}}$
= $\frac{11\sqrt{3} + 10}{2\sqrt{3}}$
= $\frac{33 + 10\sqrt{3}}{6}$
$\therefore$ The correct answer is option A.
20) Answer (D)
Let’s assume the amount obtained by Sona is 25y.
The amount obtained by Mona is 92% of the amount obtained by Sona.
Then the amount obtained by Mona = 25y of 92%
= $25y \times \frac{92}{100}$
= $y \times \frac{92}{4}$
= 23y
The ratio between the amount obtained by Mona and Raj is 23:39 respectively.
So we can say that the amount obtained by Raj will be 39y.
If the difference between the amount obtained by Sona and Raj is Rs. 434 .
39y – 25y = 434
14y = 434
y = 31
The amount obtained by Mona = 23y = $23\times31$
= Rs. 713
Hence, option d is the correct answer.
DOWNLOAD APP FOR SSC FREE MOCKS
We hope this Maths Questions pdf for SSC CGL Tier 2 exam will be highly useful for your Preparation.