Linear Equation Questions For SSC GD PDF Set – 2
SSC GD Constable Linear Equation Question paper with answers download PDF based on SSC GD exam previous papers. 40 Very important Linear Equation questions for GD Constable.
DOWNLOAD SSC GD LINEAR EQUATION QUESTIONS PDF
GET 20 SSC GD MOCK FOR JUST RS. 117
Download SSC GD Important Questions PDF
1500+ Must Solve Questions for SSC Exams (Question bank)
Question 1: Find the number of factors of 13x if (7-$\frac{4x}{3}$)($\frac{3}{2}$)=$\frac{x}{6}$.
a) 12
b) 4
c) 8
d) 6
Question 2: Find the value of $\ \sqrt{30+\sqrt{30}+…}$
a) 5
b) 3
c) 6
d) 7
Question 3: $2\frac{1}{5}x^{2}\ $= 2750, find the value of x ?
a) 25
b) $25\sqrt{3}$
c) $25\sqrt{2}$
d) 20
Question 4: Sin A + Sin$^{2}\ $A = 1, then the value of cos$^{2}\ $A + cos$^{4}\ $A is
a) 2
b) $\frac{2}{3}$
c) $1\frac{1}{2}$
d) 1
Question 5: If X = $\ \sqrt[3]{5}\ $+ 2, then the value of $\ x^{3}-6x^{2}\ $+ 12x – 13 is
a) -1
b) 1
c) 2
d) 0
Download SSC GD FREE PREVIOUS PAPERS
Question 6: If 2x + $\ \frac{2}{x}\ $= 3 then the value of $\ x^{3}+\frac{1}{x^{3}}$+ 2 is
a) -$\frac{9}{8}$
b) -$\frac{25}{8}$
c) $\frac{7}{8}$
d) 11
Question 7: If$\ a^{2}+b^{2}+c^{2}$= 2(a-b-c)-3, then the value of 4a – 3b + 5c is
a) 2
b) 3
c) 5
d) 6
Question 8: The value of$\ \frac{3\sqrt{2}}{(\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{6})}-\frac{4\sqrt{3}}{(\sqrt{6}+\sqrt{2})}+\frac{\sqrt{6}}{(\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{3})}\ $is
a) $\sqrt{2}$
b) 0
c) $\sqrt{3}$
d) $\sqrt{6}$
Question 9: The value of $\sqrt{2\sqrt[3]{4}\sqrt{2\sqrt[3]{4}}\sqrt[4]{2\sqrt[3]{4}}…..}$ is
a) $2\sqrt[3]4$
b) $\sqrt{2\sqrt[3]4}$
c) $2\sqrt4$
d) $\sqrt[3]4$
Question 10: The value of cosec$^{2}\ 18^\circ\ – \frac{1}{cot^{2}72^\circ}\ $is
a) $\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$
b) $\frac{\sqrt{2}}{3}$
c) $\frac{1}{2}$
d) 1
DOWNLOAD APP TO ACESS DIRECTLY ON MOBILE
Question 11: If$\ x^{2}$- 3x + 1 = 0, then the value of $\ x^{5}+\frac{1}{x^{5}}\ $is equal to
a) 87
b) 123
c) 135
d) 201
Question 12: The value of 0.65 x 0.65 + 0.35 x 0.35+0.70 x 0.65 is
a) 1.75
b) 1.00
c) 1.65
d) 1.55
Question 13: The value of $\frac{(75.8)^{2}-(35.8)^{2}}{40}$ is
a) 121.6
b) 40
c) 160
d) 111.6
Question 14: If $tan(\theta)tan(5\theta)=1$, then what is the value of $sin 2\theta$ ?
a) $0$
b) $\frac{1}{2}$
c) $1\sqrt2$
d) $\frac{\sqrt3}{2}$
Question 15: What is the simplified value of $\ \frac{2sin^{3}\ \theta\ – sin\theta}{cos\theta\ -\ 2\ cos^{3}\ \theta}$?
a) tan θ
b) sin θ
c) cos θ
d) cot θ
SSC
Download SSC GD Constable Syllabus PDF
Question 16: If$\ \frac{x-xtan^{2}15^\circ}{1+tan^{2}15^\circ}$= sin $60^\circ\ $+ cos 30$^\circ\ $, then what is then what is the value of x?
a) 2
b) -1
c) -2
d) 1
Question 17: What is the simplified value of$\ \sqrt{\frac{sec^{2} \theta+cosec^{2} \theta}{4}}$?
a) cosec 2θ
b) sec 2θ
c) cosec θ sec θ
d) tan θ
Question 18: The side QR of ΔPQR is produced to S. If ∠PRS = 105° and ∠Q = (1/2)∠P, then what is the value of ∠P?
a) 45
b) 60
c) 70
d) 75
Question 19: In the given figure, O is the center of the circle, $\angle$CAO = 35$^\circ$. What is the value (in degrees) of $\ \angle$AOB?
a) 90
b) 110
c) 160
d) 130
Question 20: In ΔABC, ∠A : ∠B : ∠C = 3 : 3 : 4. A line parallel to BC is drawn which touches AB and AC at P and Q respectively. What is the value of ∠AQP – ∠APQ?
a) 12
b) 18
c) 24
d) 36
Question 21: If $x = 5 – \frac{1}{x} $, then what is the value of $x^{5} + \frac{1}{x^{5}}$?
a) 625
b) 3125
c) 2525
d) 2500
Question 22: If $x^{3} – y^{3} = 112$ and $x – y = 4$, then what is the value of $x^{2} + y^{2}$?
a) 16
b) 20
c) 24
d) 28
Question 23: If $3x – \frac{1}{3x} = 9$, then what is the value of $x^{2} + \frac{x^2}{81}$?
a) 7
b) 83/9
c) 11
d) 121/9
Question 24: If $x^{4}+\frac{1}{x^{4}}= 198$ and $x>0$, then what is the value of $x^{2}-\frac{1}{x^{2}}$?
a) $14$
b) $2\sqrt{7}$
c) $10\sqrt{2}$
d) $10$
Question 25: If $x + y = 4$, then what is the value of $x^{3} +y^{3} +12xy$?
a) 16
b) 32
c) 64
d) 256
Question 26: If $N=(\frac{\sqrt{7}-\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{7}+\sqrt{5}})$, then what is the value of $\frac{1}{N}$ ?
a) $6-\sqrt{35}$
b) $6+\sqrt{35}$
c) $7+\sqrt{35}$
d) $7-\sqrt{35}$
Question 27: If cosec θ + 3 sec θ = 5 cosec θ, then what is the value of cot θ?
a) 4/3
b) 3/4
c) 1/√3
d) √3
Question 28: What is the simplified value of $\ \frac{7}{sec^{2} \theta}+ \frac{3}{1+cot^{2} \theta}+ 4\ sin^{2} \theta$?
a) 3
b) 4
c) 5
d) 7
Question 29: If √5 tan θ = 5 sin θ, then what is the value of (sin$^{2}$ θ – cos$^{2}$θ)?
a) 3/5
b) 1/5
c) 4/5
d) 2/5
Question 30: If tan $\ \theta\ $= $\ \frac{2}{3}\ $, then what is the value of $\ \frac{15sin^{2} \theta-3cos^{2} \theta}{5sin^{2} \theta+3cos^{2} \theta}$?
a) $\frac{33}{32}$
b) $\frac{11}{29}$
c) $\frac{33}{47}$
d) $\frac{11}{32}$
Question 31: In an isosceles triangle PQR, ∠P = 130$^\circ$. If I is the in-centre of the triangle, then what is the value (in degrees) of ∠QIR?
a) 130
b) 120
c) 155
d) 165
Question 32: In the given figure, EF = CE = CA, What is the value (in degrees) of $\angle$EAC?
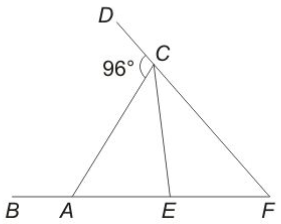
a) 58
b) 64
c) 72
d) 32
Question 33: In the given figure, O is the center of the circle, $\ \angle$PQR = 100$^\circ\ $and $\angle$STR = 105$^\circ$. What is the value (in degrees) of $\ \angle$OSP?
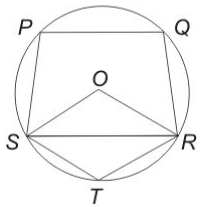
a) 95
b) 45
c) 75
d) 65
Question 34: What is the value of $\ \frac{(a^{2}+b^{2})(a-b)-(a-b)^{2}}{a^{2}b-ab^{2}}$?
a) 0
b) 1
c) -1
d) 2
100+ Free GK Tests for SSC Exams
Question 35: If $\ x^{2}\ – 3x + 1 = 0$, then what is the value of $\ x^{4}\ $+ $\ \frac{1}{x^{4}}$?
a) 11
b) 18
c) 47
d) 51
Question 36: If $\ \frac{3x-1}{x}+\frac{5y-1}{y}+\frac{7z-1}{z}$= 0, then what is the value of $\ \frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{y}+\frac{1}{z}\ $?
a) -3
b) 0
c) 15
d) 21
Question 37: If $x^{2}- 2\sqrt{10}x+ 1 = 0$, then what is the value of $x – \frac{1}{x}$?
a) 4
b) 6
c) 3
d) 5
Question 38: If $x^{2} -7x + 1 = 0$, then what is the value of $x + \frac{1}{x}$?
a) 7
b) 3
c) 51
d) 47
Question 39: If the angles of a triangle are (2x – 8)$^{o}$, (2x + 18)$^{o}$and 6x$^{o}$. What is the value of 3x (in degrees)?
a) 17
b) 34
c) 51
d) 60
Question 40: What is the value of $999\frac{1}{3}+999\frac{1}{6}+999\frac{1}{12}+999\frac{1}{20}+999\frac{1}{30}$?
a) $999\frac{1}{6}$
b) $999\frac{5}{6}$
c) $4995\frac{1}{6}$
d) $4995\frac{4}{6}$
Answers & Solutions:
1) Answer (D)
solving the equation for x,
We get $\frac{21}{2}$=$2x+\frac{x}{6}$
$\frac{21}{2}$=$\frac{13x}{6}$
$x$=$\frac{63}{13}$
$13x$=63
Factorising 63 we get 63=$3^{2}\times 7$
Number of factors=(2+1)(1+1)
=6
2) Answer (C)
Let X=$ \sqrt{30+\sqrt{30}+…}$
Above equation can be written as
X=$\Rightarrow\sqrt{30+X}$
Squaring on both sides
$X^{2}$=30+X
$X^{2}$-X-30=0
$X^{2}$-6X+5X-30=0
X(X-6)+5(X-6)=0
(X-6)(X+5)=0
X=-5,6
Taking positive value
X=6
3) Answer (C)
$2\frac{1}{5}x^{2}=2750$
==> $\frac{11}{5}x^{2}=2750$
==> $x^{2}= \frac{2750\times5}{11}$
==> $x^{2}= 1250$
==> $x = \sqrt{1250}=\sqrt{625\times2}$
==> $x = 25\sqrt{2}$
4) Answer (D)
Given sin A+$sin^{2}$ A=1
==> sin A = 1-$sin^{2}$ A
==> sin A = $cos^{2}$ A ($\because cos^{2}A+sin^{2}A$=1)
$cos^{2}$ A=sin A ==> $cos^{4}A$=$sin^{2}A $
$\therefore cos^{2}A+cos^{4}A=1 ( \because sin A+sin^{2}A=1)$
5) Answer (D)
Given x=\sqrt[3]{5}+2
$\ x^{3}-6x^{2}\ $+ 12x – 13
= $(\sqrt[3]{5}+2)^{3}-6(\sqrt[3]{5}+2)^{2}+12(\sqrt[3]{5}+2)-13$
= $(5+8+6\times5^{\frac{2}{3}}+12\times5^{\frac{1}{3}})-6[5^{\frac{1}{3}}+4+4\times5^{\frac{1}{3}}]+12(5^{\frac{1}{3}}+2)-13$
= $13+6\times5^{\frac{2}{3}}+12\times5^{\frac{1}{3}}-6\times5^{\frac{2}{3}}-24-24\times5^{\frac{1}{3}}+12\times5^{\frac{1}{3}}+24-13$
= 0
6) Answer (C)
Given 2x+$\frac{1}{x} =$ 3
2(x+$\frac{1}{x}) =$ 3
$\Rightarrow$ x+$\frac{1}{x} = \frac{3}{2}$
Cubing on both sides
(x+$\frac{1}{x})^{3} = \frac{27}{8}$
x$^{3}$+$\frac{1}{x^{3}}$+3$\times$x$\times$ $\frac{1}{x}$(x+$\frac{1}{x}$) $= \frac{27}{8}$
$\Rightarrow x^{3}+\frac{1}{x^{3}}+3(\frac{3}{2}) = \frac{27}{8}$
$\Rightarrow x^{3}+\frac{1}{x^{3}} = \frac{27}{8}-\frac{9}{2} = \frac{-9}{8}$
$x^{3}+\frac{1}{x^{3}}+2 = \frac{-9}{8}+2 = \frac{7}{8}$
7) Answer (A)
$\ a^{2}+b^{2}+c^{2}$= 2(a-b-c)-3
We can write the above equation as
$ a^{2}-2a+1+b^{2}+2b+1+c^{2}+2c+1$=0
$\Rightarrow (a-1)^{2}+(b+1)^{2}+(c+1)^{2}$=0
$(a-1)^{2}$=0$\Rightarrow$a=1
$(b+1)^{2}$=0$\Rightarrow$ b=-1
$(c+1)^{2}$=0$\Rightarrow$ c=-1
4a-3b+5c= 4(1)-3(-1)+5(-1)=4+3-5=2
8) Answer (B)
$\frac{3\sqrt{2}}{(\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{6})}-\frac{4\sqrt{3}}{(\sqrt{6}+\sqrt{2})}+\frac{\sqrt{6}}{(\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{3})}$
= $\frac{6\sqrt{6}+18+6\sqrt{2}+6\sqrt{3}-(12\sqrt{2}+24+12\sqrt{3}+12\sqrt{6})+6\sqrt{3}+6+6\sqrt{6}+6\sqrt{2}}{(\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{6})(\sqrt{6}+\sqrt{2})(\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{3})}$
= $\frac{6\sqrt{6}+18+6\sqrt{2}+6\sqrt{3}-12\sqrt{2}-24-12\sqrt{3}-12\sqrt{6}+6\sqrt{3}+6+6\sqrt{6}+6\sqrt{2}}{(\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{6})(\sqrt{6}+\sqrt{2})(\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{3})}$
=0
9) Answer (A)
To find : $y=\sqrt{2\sqrt[3]{4}\sqrt{2\sqrt[3]{4}}\sqrt[4]{2\sqrt[3]{4}}…..}$
Let $2\sqrt[3]4=x$
=> $y=\sqrt{(x)\times(\sqrt{x})\times(\sqrt[4]{x})\times…….}$
=> $y^2=(x)^{[1+\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{4}+……+\infty]}$
Now, sum of infinite G.P. = $\frac{a}{(1-r)}$, where first term = $a=1$ and common ratio = $r=\frac{1}{2}$
=> $y^2=(x)^{\frac{1}{1-\frac{1}{2}}}$
=> $y^2=(x)^2$
=> $y=x$
$\therefore$ $\sqrt{2\sqrt[3]{4}\sqrt{2\sqrt[3]{4}}\sqrt[4]{2\sqrt[3]{4}}…..}=2\sqrt[3]4$
=> Ans – (A)
10) Answer (D)
cosec$^{2}\ 18^\circ\ – \frac{1}{cot^{2}72^\circ}\ $
= cosec$^{2} 18^\circ – tan^{2} 72^\circ$ ($\because \frac{1}{cot^{2} \ominus}$=$tan^{2}\ominus$)
= cosec$^{2} 18^\circ$ – $tan^{2} (90-72)^\circ$
= cosec$^{2} 18^\circ$ – $sec^{2} 18^\circ$ ($\because sec^{2}\ominus= tan^{2}(90^\circ-\ominus)$)
cosec$^{2} 18^\circ$ – $sec^{2} 18^\circ$=1($\because cosec^{2} \ominus$ – $sec^{2} \ominus$=1)
11) Answer (B)
$x^{2}-3x+1$=0
Taking ‘x’ common
x(x-3+$\frac{1}{x})$=0
$\Rightarrow x+\frac{1}{x}$=$3\rightarrow(1)$
Squaring on both sides
$x^{2}+\frac{1}{x^{2}}+2\times x\times\frac{1}{x}$=9
$\Rightarrow x^{2}+\frac{1}{x^{2}}$=$7\rightarrow(2)$
Cubing equation(1) on both sides
$x^{3}+\frac{1}{x^{3}}+3\times x\times\frac{1}{x}(x+\frac{1}{x})$=27
$x^{3}+\frac{1}{x^{3}}$+$3\times 1\times3$=27($\because x+\frac{1}{x}$=3)
$x^{3}+\frac{1}{x^{3}}$=27-9=$18\rightarrow(3)$
Squaring equation(2) on both sides
$x^{4}+\frac{1}{x^{4}}+2\times x^{2}\times\frac{1}{x^{2}}$=49
$x^{4}+\frac{1}{x^{4}}$=$47\rightarrow(4)$
Multiplying equation(1) and equation(4)
$(x^{4}+\frac{1}{x^{4}})(x+\frac{1}{x}$)=$47\times3$
$x^{5}+\frac{1}{x^{5}}+x^{3}+\frac{1}{x^{3}}$=$47\times3$=141
$x^{5}+\frac{1}{x^{5}}+18$=141($\because x^{3}+\frac{1}{x^{3}}$)
$\therefore x^{5}+\frac{1}{x^{5}}$=123
12) Answer (B)
Expression : $(0.65\times0.65)+(0.35\times0.35)+(0.70\times0.65)$
= $(0.65)^2+(0.35)^2+2(0.35)(0.65)$
Comparing with : $(x)^2+(y)^2+2(x)(y)=(x+y)^2$
= $(0.65+0.35)^2=(1)^2=1$
=> Ans – (B)
13) Answer (D)
$\frac{75.8^{2}-35.8^{2}}{40}$=$\frac{(75.8+35.8)(75.8-35.8)}{40}$
=$\frac{111.6\times40}{40}$=111.6
14) Answer (B)
Given : $tan(\theta)tan(5\theta)=1$
Using, $tan(A+B)=\frac{tanA+tanB}{1-tanAtanB}$
$tan(\theta+5\theta)=\frac{tan(\theta)+tan(5\theta)}{1-tan(\theta)tan(5\theta)}$
=> $tan(6\theta)=\frac{tan(\theta)+tan(5\theta)}{1-1}$
=> $tan(6\theta)=\infty$
=> $tan(6\theta)=tan(90^\circ)$
=> $6\theta=90^\circ$
=> $\theta=\frac{90^\circ}{6}=15^\circ$
$\therefore$ $sin(2\theta)=sin(2\times15^\circ)$
= $sin(30^\circ)=\frac{1}{2}$
=> Ans – (B)
15) Answer (A)
Expression : $\ \frac{2sin^{3}\ \theta\ – sin\theta}{cos\theta\ -\ 2\ cos^{3}\ \theta}$
= $\ \frac{sin\ \theta(2sin^{2}\ \theta\ – 1)}{cos\ \theta(2 -\ 2\ cos^{2}\ \theta)}$
= $\frac{sin\ \theta(cos2\ \theta)}{cos\ \theta(cos2\ \theta)}$
= $\frac{sin\ \theta}{cos\ \theta}=tan\ \theta$
=> Ans – (A)
16) Answer (A)
$tan15^\circ=\frac{\sqrt3-1}{\sqrt3+1}$
Expression = $\ \frac{x-xtan^{2}15^\circ}{1+tan^{2}15^\circ}$= sin $60^\circ\ $+ cos 30$^\circ\ $
=> $\ \frac{x(1-tan^{2}15^\circ)}{1+tan^{2}15^\circ}= \frac{\sqrt3}{2}+\frac{\sqrt3}{2}$
=> $x\times\frac{1-(\frac{\sqrt3-1}{\sqrt3+1})^2}{1+(\frac{\sqrt3-1}{\sqrt3+1})^2}=\sqrt3$
=> $x\times\frac{(\sqrt3+1)^2-(\sqrt3-1)^2}{(\sqrt3+1)^2+(\sqrt3-1)^2}=\sqrt3$
=> $x\times\frac{(3+1+2\sqrt3)-(3+1-2\sqrt3)}{(3+1+2\sqrt3)+(3+1-2\sqrt3)}=\sqrt3$
=> $x\times\frac{4\sqrt3}{8}=\sqrt3$
=> $x=\frac{8}{4}=2$
=> Ans – (A)
17) Answer (A)
Expression = $\ \sqrt{\frac{sec^{2} \theta+cosec^{2} \theta}{4}}$
= $\ \sqrt{\frac{(\frac{1}{cos^2\ \theta})+(\frac{1}{sin^2\ \theta})}{4}}$
= $\ \sqrt{\frac{(\frac{sin^2\ \theta+cos^2\ \theta)}{sin^2\ \theta.cos^2\ \theta}}{4}}$
= $\sqrt{\frac{1}{4sin^2\ \theta cos^2\ \theta}}$
= $\sqrt{(\frac{1}{2sin\ \theta cos\ \theta})^2}$
= $\frac{1}{sin2\theta}=cosec2\theta$
=> Ans – (A)
18) Answer (C)
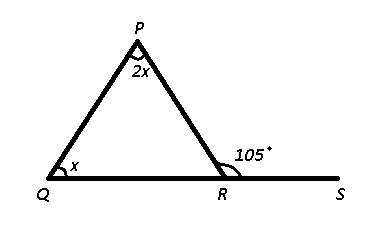
Let $\angle Q=x$, => $\angle P=2x$
Using exterior angle property in $\triangle$ PQR,
=> $\angle$ P + $\angle$ Q = $\angle$ PRS
=> $2x+x=105^\circ$
=> $x=\frac{105^\circ}{3}=35^\circ$
$\therefore$ $\angle P=2\times35^\circ=70^\circ$
=> Ans – (C)
19) Answer (C)
20) Answer (B)
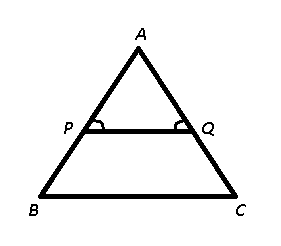
Given : ∠A : ∠B : ∠C = 3 : 3 : 4 and PQ is parallel to BC
To find : ∠AQP – ∠APQ = ?
Solution : Let $\angle A=3x$, $\angle B=3x$ and $\angle C=4x$
Thus, in $\triangle$ ABC,
=> $\angle A+\angle B+\angle C=180^\circ$
=> $3x+3x+4x=180^\circ$
=> $x=\frac{180^\circ}{10}=18^\circ$
$\because$ PQ $\parallel$ BC, => $\angle$ APQ = $\angle$ B and $\angle$ AQP = $\angle$ C (Corresponding angles)
$\therefore$ $\angle$ AQP – $\angle$ APQ = $4x-3x=x=18^\circ$
=> Ans – (B)
21) Answer (C)
Given : $x=5-\frac{1}{x}$
=> $x+\frac{1}{x}=5=k$
Now, $x^5+\frac{1}{x^5}=[(x^3+\frac{1}{x^3})\times(x^2+\frac{1}{x^2})]-(x+\frac{1}{x})$
= $[(x+\frac{1}{x})^3-3(x+\frac{1}{x})\times(x+\frac{1}{x})^2-2(x)(\frac{1}{x})]-(x+\frac{1}{x})$
= $[(k^3-3k)\times(k^2-2)]-(k)$
= $[(125-15)\times(25-2)]-(5)$
= $(110\times23)-5$
= $2530-5=2525$
=> Ans – (C)
SSC GD Important Questions & Answers PDF
22) Answer (C)
Given : $x^3-y^3=112$ ————–(i)
Also, $x-y=4$ ————-(ii)
Cubing both sides, we get :
=> $(x-y)3=(4)^3$
=> $(x^3-y^3)-3(x)(y)(x-y)=64$
Substituting values from equations (i) and (ii),
=> $112-3xy(4)=64$
=> $12xy=112-64=48$
=> $xy=\frac{48}{12}=4$ ———–(iii)
Now, squaring equation (ii), we get :
=> $x^2+y^2-2xy=16$
=> $x^2+y^2=16+8=24$
=> Ans – (C)
23) Answer (B)
Given : $3x-\frac{1}{3x}=9$
Dividing both sides by 3, => $x-\frac{1}{9x}=3$
Squaring both sides, we get :
=> $(x-\frac{1}{9x})^2=(3)^2$
=> $x^2+\frac{1}{81x^2}-2(x)(\frac{1}{9x})=9$
=> $(x^2+\frac{1}{81x^2})-\frac{2}{9}=9$
=> $(x^2+\frac{1}{81x^2})=9+\frac{2}{9}$
=> $(x^2+\frac{1}{81x^2})=\frac{83}{9}$
=> Ans – (B)
24) Answer (A)
Given : $\ x^{4}+\frac{1}{x^{4}}\ =198$
=> $(x^2-\frac{1}{x^2})^2+2(x^2)(\frac{1}{x^2})=198$
=> $(x^2-\frac{1}{x^2})^2=198-2=196$
=> $x^2-\frac{1}{x^2}=\sqrt{196}=14$
=> Ans – (A)
25) Answer (C)
Given : $x+y=4$ ———–(i)
Cubing both sides, we get :
=> $(x+y)^3=(4)^3$
=> $x^3+y^3+3xy(x+y)=64$
=> $x^3+y^3+3xy(4)=64$
=> $x^3+y^3+12xy=64$
=> Ans – (C)
26) Answer (B)
Given : $N=\frac{\sqrt7-\sqrt5}{\sqrt7+\sqrt5}$
=> $\frac{1}{N}=\frac{\sqrt7+\sqrt5}{\sqrt7-\sqrt5}$
Rationalizing the denominator, we get :
= $\frac{\sqrt7+\sqrt5}{\sqrt7-\sqrt5}\times\frac{\sqrt7+\sqrt5}{\sqrt7+\sqrt5}$
= $\frac{(\sqrt7+\sqrt5)^2}{(\sqrt7-\sqrt5)(\sqrt7+\sqrt5)}$
= $\frac{7+5+2(\sqrt7)(\sqrt5)}{7-5}$
= $\frac{12+2\sqrt{35}}{2}=6+\sqrt{35}$
=> Ans – (B)
27) Answer (B)
Given : $cosec\theta+3sec\theta=5cosec\theta$
=> $3sec\theta=5cosec\theta-cosec\theta$
=> $3sec\theta=4cosec\theta$
=> $\frac{3}{cos\theta}=\frac{4}{sin\theta}$
=> $\frac{cos\theta}{sin\theta}=\frac{3}{4}$
=> $cot\theta=\frac{3}{4}$
=> Ans – (B)
28) Answer (D)
Expression : $\ \frac{7}{sec^{2} \theta}+ \frac{3}{1+cot^{2} \theta}+ 4\ sin^{2} \theta$
= $7cos^2\ \theta+\frac{3}{cosec^2\ \theta}+4sin^2\ \theta$
= $7cos^2\ \theta+3sin^2\ \theta+4sin^2\ \theta$
= $7cos^2\ \theta+7sin^2\ \theta$
= $7(cos^2\ \theta+sin^2\ \theta)$
= $7\times1=7$
=> Ans – (D)
29) Answer (A)
Given : $\sqrt5tan\ \theta=5sin\ \theta$
=> $\frac{sin\ \theta}{cos\ \theta}=\sqrt5sin\ \theta$
=> $cos\ \theta=\frac{1}{\sqrt5}$
=> $cos^2\ \theta=\frac{1}{5}$ —————(i)
Now, $sin^2\ \theta=1-cos^2\ \theta$
=> $sin^2\ \theta=1-\frac{1}{5}=\frac{4}{5}$ ————–(ii)
Subtracting equation (i) from (ii), we get :
$\therefore$ $(sin^2\ \theta-cos^2\ \theta)=\frac{4}{5}-\frac{1}{5}=\frac{3}{5}$
=> Ans – (A)
30) Answer (C)
Given : $tan\ \theta=\frac{2}{3}$
=> $\frac{sin\ \theta}{cos\ \theta}=\frac{2}{3}$
Let $sin\ \theta=2$ and $cos\ \theta=3$
To find : $\ \frac{15sin^{2} \theta-3cos^{2} \theta}{5sin^{2} \theta+3cos^{2} \theta}$
= $\frac{15(2)^2-3(3)^2}{5(2)^2+3(3)^2}$
= $\frac{60-27}{20+27}$
= $\frac{33}{47}$
=> Ans – (C)
31) Answer (C)
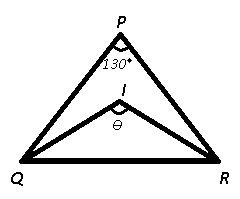
Given : I is the incentre of $\triangle$ PQR and $\angle$ BAC = 130°
To find : $\angle$ QIR = $\theta$ = ?
Incentre of a triangle = $90^\circ+\frac{\angle P}{2}$
=> $\theta=90^\circ+\frac{130^\circ}{2}$
=> $\theta=90^\circ+65^\circ$
=> $\theta=155^\circ$
=> Ans – (C)
32) Answer (B)

Given : EF = CE = CA
=> $\angle$ CAE = $\angle$ CEA = $x$ and $\angle$ ECF = $\angle$ EFC = $y$
To find : $\angle$ EAC = $x=?$
Solution : Using exterior angle property, => $\angle$ CAE + $\angle$ CFE = $\angle$ ACD
=> $x+y=96^\circ$ —————–(i)
Also, $\angle$ CEF = $(180^\circ-2y)=180^\circ-x$
=> $x=2y$ ————(ii)
Substituting it in equation (i), => $2y+y=3y=96^\circ$
=> $y=\frac{96}{3}=32^\circ$
$\therefore$ $x=2\times32=64^\circ$
=> Ans – (B)
33) Answer (D)
Given : $\ \angle$PQR = 100$^\circ\ $and $\angle$STR = 105$^\circ$
To find : $\ \angle$OSP = ?
Solution : Quadrilateral PQRS is cyclic quadrilateral, hence opposite angles are supplementary.
=> $\angle$ PQR + $\angle$ PSR = $180^\circ$
=> $\angle$ PSR = $180^\circ-100^\circ=80^\circ$ ————–(i)
Also, angle at the centre is double the angle at any point on the circumference of the circle in the same segment.
=> reflex ($\angle$ SOR) = $2$ $\times$ $\angle$ STR
=> reflex ($\angle$ SOR) = $2\times105^\circ=210^\circ$
Thus, $\angle$ SOR = $360^\circ-210^\circ=150^\circ$
Now, in $\triangle$ SOR, OS = OR = radius
=> $\angle$ OSR = $\angle$ ORS = $15^\circ$ ———-(ii)
Subtracting equation (ii) from (i), we get :
$\therefore$ $\angle$ OSP = $80^\circ-15^\circ=65^\circ$
=> Ans – (D)
34) Answer (D)
Expression : $\ \frac{(a^{2}+b^{2})(a-b)-(a-b)^{2}}{a^{2}b-ab^{2}}$
= $\ \frac{(a-b)[(a^{2}+b^{2})-(a-b)]}{(ab)(a-b)}$
= $\frac{(a^2+b^2)-(a-b)}{ab}$
= $\frac{(a-b)^2+2ab-(a-b)}{ab}$
35) Answer (C)
Given : $x^2-3x+1=0$
Dividing both sides by $’x’$
=> $x+\frac{1}{x}=3$
Squaring both sides, we get :
=> $x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}+2(x)(\frac{1}{x})=9$
=> $x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}=9-2=7$
Again squaring both sides,
=> $x^4+\frac{1}{x^4}+2(x^2)(\frac{1}{x^2})=49$
=> $x^4+\frac{1}{x^4}=49-2=47$
=> Ans – (C)
36) Answer (C)
Given : $\ \frac{3x-1}{x}+\frac{5y-1}{y}+\frac{7z-1}{z}=0$
=> $(3-\frac{1}{x})+(5-\frac{1}{y})+(7-\frac{1}{z})=0$
=> $\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{y}+\frac{1}{z}=3+5+7$
=> $\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{y}+\frac{1}{z}=15$
=> Ans – (C)
37) Answer (B)
Given : $x^2-2\sqrt{10}x+1=0$
Dividing both sides by $’x’$
=> $x+\frac{1}{x}=2\sqrt{10}$
Squaring both sides, we get :
=> $x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}+2(x)(\frac{1}{x})=40$
=> $x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}=40-2=38$
=> $(x-\frac{1}{x})^2+2(x)(\frac{1}{x})=38$
=> $(x-\frac{1}{x})^2=38-2=36$
=> $x-\frac{1}{x}=\sqrt{36}=6$
=> Ans – (B)
38) Answer (A)
Given : $x^2-7x+1=0$
Dividing both sides by $’x’$
=> $x-7+\frac{1}{x}=0$
=> $x+\frac{1}{x}=7$
=> Ans – (A)
39) Answer (C)
Sum of angles of a triangle = $180^\circ$
=> $(2x-8)^\circ+(2x+18)^\circ+(6x)^\circ=180^\circ$
=> $10x+10=180$
=> $10x=180-10=170$
=> $x=\frac{170}{10}=17$
$\therefore$ $3x=3\times17=51$
=> Ans – (C)
40) Answer (D)
Expression : $999\frac{1}{3}+999\frac{1}{6}+999\frac{1}{12}+999\frac{1}{20}+999\frac{1}{30}$
= $(999+999+999+999+999)+(\frac{1}{3}+\frac{1}{6}+\frac{1}{12}+\frac{1}{20}+\frac{1}{30})$
= $(4995)+(\frac{20+10+5+3+2}{60})$
= $4995+\frac{40}{60}$
= $4995\frac{4}{6}$
=> Ans – (D)
Download SSC GD Previous Papers PDF
DOWNLOAD APP FOR SSC FREE MOCKS
We hope this Linear Equation questions for SSC GD will be highly useful for your preparation.





